Lesson 16: Subtypes
Overview:
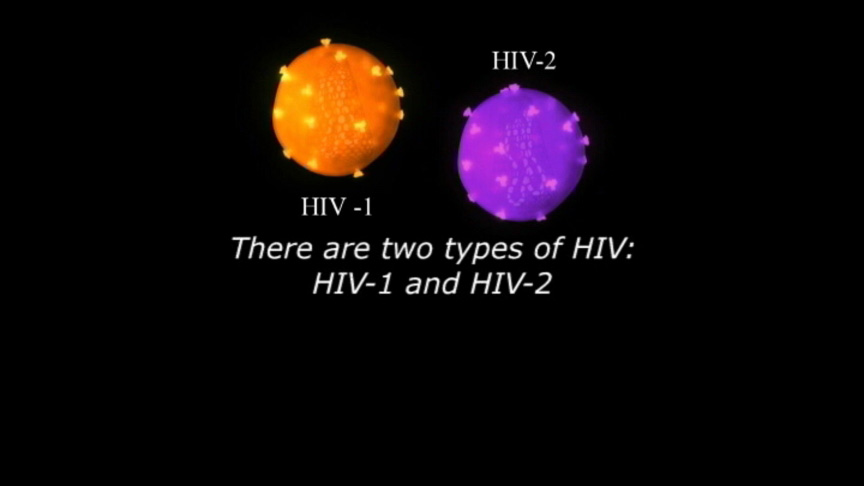
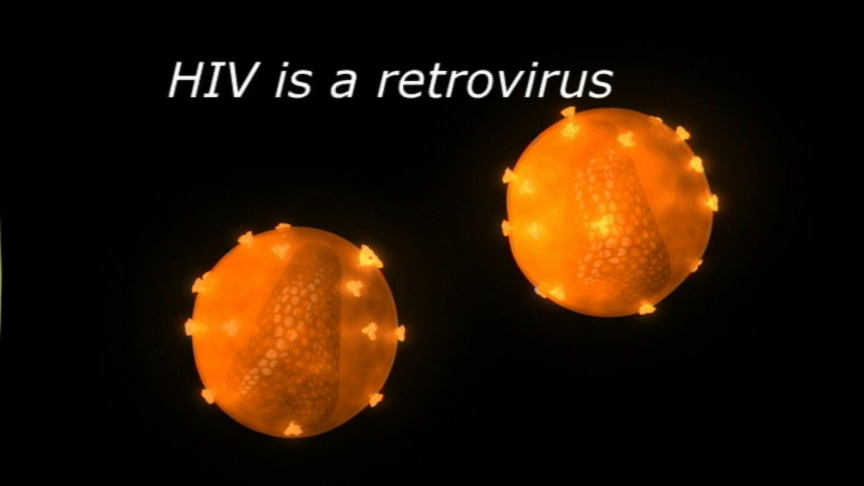
HIV is a retrovirus—replicates in the host cell—and mutates very rapidly. These mutations can be either weaker versions or more disastrously, stronger versions that are resistant to current drug treatments. This rapid mutation is partly why HIV/AIDS has been so catastrophic. There are to major types of HIV, 1 and 2. Each major type is broken down by groups and then within a group there are subtypes. So, for example, HIV-1, cause of the global pandemic, has four groups: M for major; O for outlier; N for non-M or non-O; and P for new discoveries that have not been classified. Group M has over ten subtypes; Subtype C, found mostly in Africa and India, is considered most infectious. The video module, “Subtypes,” examines HIV, its subtypes and the speed at which it mutates.
Download Materials:
PDF Downloads:
Lesson 16 – Subtypes (Grayscale)
Lesson 16 – Subtypes (Color)
Lesson 16 – Subtypes (Color Ink Saving)
Video Downloads:
MAC .m4v file
PC .wmv file